
Prices for Brent oil in the second half 2015 should rise to $75/bbl., but not above $90/bbl., and in 2016 the price will be higher than $90/bbl. This conclusion was made by Turan agency on the basis of analysis of the political, but not economic reasons for the sharp fall in oil prices.
The fall in oil prices was triggered by the US decision on the release to the market additional volumes of oil to accelerate reforms during systemic crisis in the authoritarian oil-dependent countries, such as Russia, Iran, Venezuela, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Nigeria, and on the other hand, to relieve pressure on the economy and consumer markets of developed countries.The allies of this strategic game of the oil producing countries, such as the Persian Gulf, where the main player is Saudi Arabia, also feel the effects of this policy, but they can survive the fall in oil prices with losses for the short term.
Saudi Arabia is increasingly dependent on oil production, and in principle it should not be advantageous for it to increase production and bring down prices, but Saudi Arabia did under the US policy, which agreed to take a constructive dialogue the above countries.
Oil prices in the US policy have always been impressive and powerful means of promoting the interests of reformatting the world order with the expansion of the area of democracy in different parts of the globe. This tool was used for the collapse of the USSR, as well as in the subsequent period to advance their goals. It is a fact, but the number of authoritarian regimes in the past 25 years was considerably reduced, and the field of democracy and developed countries has increased notably. And most of the countries on different continents is in the transactional period from authoritarianism to democracy.
In this regard, Russia as the successor of the USSR, the support of nuclear power, remains a defendant in reformatting pivot system. And the transformation of Russia into a democratic state partnership remains a key priority objective of the policy of democratization.
After the collapse of the Soviet Union, the oil prices remained low, forcing the post-Soviet countries, especially Russia, rapidly develop the private sector and privatization of enterprises, although with no effective results. On the other hand, against this background was observed a notable decrease of influence of the central government and the strengthening of the internal contradictions between reformists and supporters of imperial traditions, as well as contradiction between the center and the regions, with domination of communist values. By 1998, the threat of losing control of the country by Yeltsin's team, the country's disintegration becomes real.
A reflection of this situation became the financial crisis of 1998, which brought the country to default. To achieve stabilization and controlling with further the anti-communist reforms become visible the contours of the new team, which became the backbone of the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service. Elite, having knowledge, possessing the information of internal and external character, vision and the ability to analyze, understanding the inevitability of reform and at the same time characterized by high loyalty to the state. Another important moment is communication and access to high foreign interests. In this sense, the ascent of Vladimir Putin was not accidental.
Oil prices, increase stably and sometimes very high after the beginning of Putin's ascent to the pinnacle of power and cyclical crises in Russia, when the oil factor became important investment factor for regular post-crisis reforms, unfortunately, not very successful.
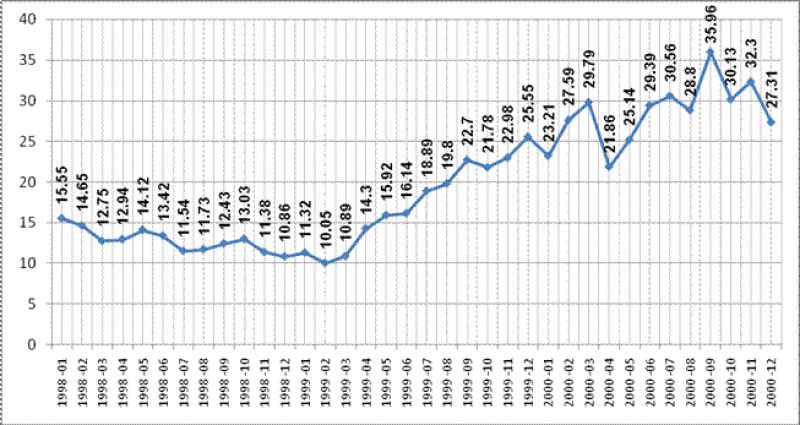
For the first time after the collapse of Soviet Union, the oil prices began to increase after Putin's appointment as secretary of the Russian Security Council in March 1999, when the price of a barrel of oil rose to $10.89, and crossed an unprecedented milestone for those years of $16/bbl. After Putin was appointed Prime Minister in August 1999, the price line is crossing $20/bbl, further rises higher. We must also bear in mind that this was preceded by the August 1998 financial crisis and anti-terrorist operation in Dagestan in September 1999 which turn in 2000 to the second Chechen war, which ended with the strengthening of Moscow's control over the North Caucasus.
Cost barrels of crude oil varieties Brent from January 1998 – to December 2000 (in USD)
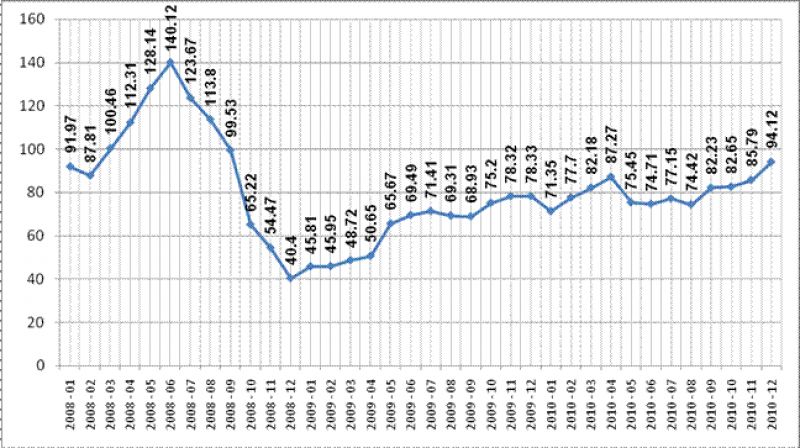
Oil prices peaked in June 2008 reached peak point - $140/bbl., and then begin to fall during the beginning of the next financial crisis and the war in Georgia, reaching the bottom in December 2008, when oil was offered at $40/bbl. After the situation in Georgia has stabilized, the government Medvedev announced a policy of modernization and reached an agreement on a range of issues with the US in May 2009, the price rose to $70/bbl.
Cost barrels of crude oil varieties Brent from January 2008 – to December 2010 (in USD)
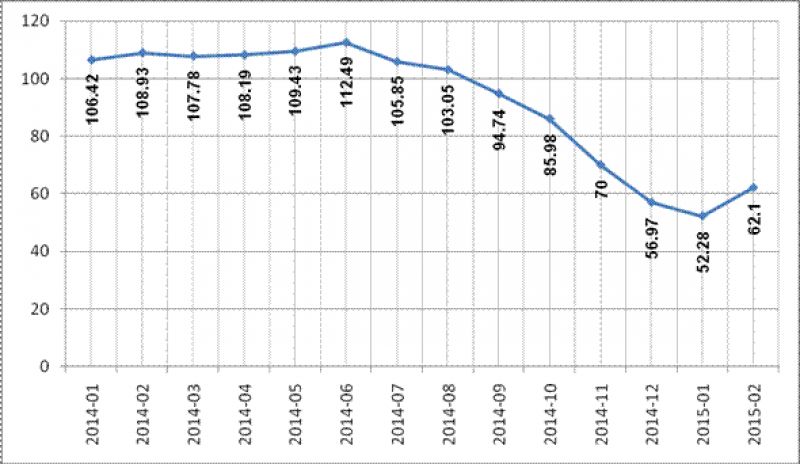
The fall in prices from $110 to $50 is also associated with the beginning of the economic crisis in Russia and another military campaign against Ukraine now.
In these periods of Russian history oil has played two important roles:
1. The fall in prices accelerated decision-making on reforming the Russian economy, create more favorable conditions for international loans, investments and multinational companies in general western, diversification of energy routes, access to energy giant oil and gas projects in Russia, Russian concessions to the former Soviet Union and in other areas of influence.
2. The increase of prices created an impressive feeding Russia's economy and stimulated investment to implement reforms and social programs.
The development of crisis stages and military campaigns as an integral part of this process showed that today's low prices are temporary and will grow in the near future. In this regard, you can mark the beginning of the transition of the military conflict in Ukraine in a peaceful course, the development of the Russian government reform package that would require international support, negotiations with the world's energy giants to jointly develop oil and gas fields in Siberia, as well as another achievement of agreements with the United States range of issues, including concessions to the diversification of routes and areas of influence.
It is noteworthy that in January the price reached the bottom $52/bbl., and rose in February to $62/bbl., after signing the Second Minsk Agreement on Ukraine.
Cost barrels of crude oil varieties Brent from January 2014 – to February 2015 (in USD)
In this analysis, it is important to say about the mechanism of the game prices. Their rise and fall encourage the growth or vice versa decline in production in the United States and Saudi Arabia, which plays a key role and sustained action in the wake of Washington's policy.
The current decline in oil prices was triggered by an increase of supply over demand due to release on the market by two players additional oil. In the first half of 2014 the USA began to produce more than 11.5 million barrels of oil and condensate per day, and become the leader in the production of liquid hydrocarbons, the study said Bank of America Merrill Lynch. Saudi Arabia during this period produced less than 11.5 million barrels. According to the International Energy Agency, today supply exceeds demand by 400 thousand barrels per day.
Gary Shilling, a well-known economist and practices, the president of consulting firm A. Gary Shilling noted that Saudi Arabia requires price more than $90/bbl. to finance its budget. But it has $726 billion foreign exchange reserves, which allows it to survive for two years, with prices less than $40/barrel.
The fact is that the share of oil revenues in the total income of the government of Saudi Arabia is nearly 92%. According to the spydell.livejournal.com, revenues from exports reached $330 billion a year. Total government revenues total $308 billion, spending - $260 billion (budget surplus $ 48 billion.) It is necessary to take into account that public spending continued to grow rapidly, particularly due to reckless spending on infrastructure dead cities and luxury hotels in the desert, not in demand, commensurate with the expenditure.
The average oil price in 2013 was higher than in 2008, but the budget surplus was reduced from $155 billion in 2008 to $48 billion in 2013, since that time, government spending grew twice.
In 2014, the planned government spending more than $ 290 billion. The average annual price of oil was around $ 97.5, and Saudi Arabia for the first time since 2009 was included in the state budget deficit.
Withdrawal windfall through the fall in oil prices could lead not only to the economic downturn, but also cause severe social unrest in society accustomed to wealth over the past 10 years.
Now the threshold for the Saudi Arabia is approximately $100/bbl., where the economy is on the brink of recession, and fiscal balance of budget can descend into deficit. The most comfortable status quo for maintaining is the price of $107- $115. At a price below $95/bbl. They will have to uncork the strategic reserves to fulfill social obligations. In this case, the United States is unlikely to prevent the collapse of the economy as a friendly Saudi Arabia and Gulf countries.
If we look at previous experience of falling and rising oil prices, we can expect price increases, no later than the beginning of autumn to the minimum required for the Russian economy - $75/bbl, and the following year more than $90/barrel for the Saudi economy and other oil-producing countries, heavily dependent on oil.
The Azerbaijani government has budgeted for 2015 the oil price of $90/bbl., likely focusing on the needs of Saudi Arabia. The government hoped, and that the price of $90/bbl will be already by the spring. This was evidenced by certain didactic tone of President Ilham Aliyev at a cabinet meeting on 10 January. But after a trip to the Davos economic forum, just two weeks later, he had to urgently revise the forecast and devalue the national currency. But this year, Aliyev, nevertheless, have to reconsider the relation to the structure of the economy and economic freedom and adopt reformist solutions to secure the regime and the country from possible shocks with the rapid fall in oil production and price volatility.



















Leave a review